Source: oxygenark
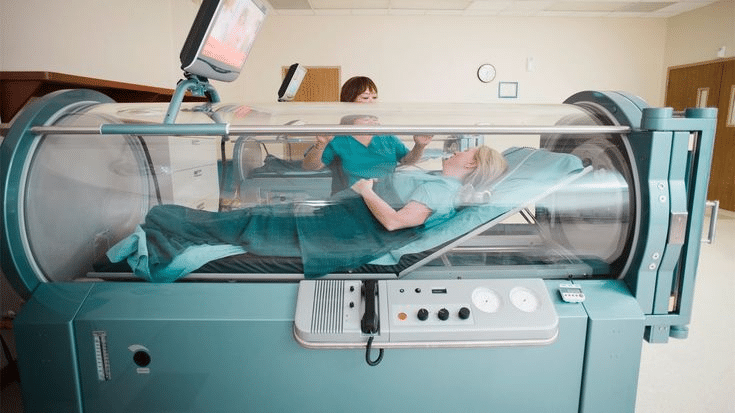
A hyperbaric chamber is an oxygen therapy device that offers numerous wellness benefits.
That’s quite a mouthful, right? So, let’s break it down without all the tech jargon.
A hyperbaric chamber is an enclosed space that, when sealed, has an atmospheric pressure 2 to 3 times higher than what we experience in normal environments. It is also designed to deliver a higher flow of oxygen compared to what you may encounter in the natural atmosphere.
But what exactly does this device do? What does oxygen therapy mean? Where and in what instances is it used? What health risks does it present? Do the risks outweigh its therapeutic benefits or is it the other way around?
We address all this and more in the blog. Read on.
Hyperbaric Chambers 101
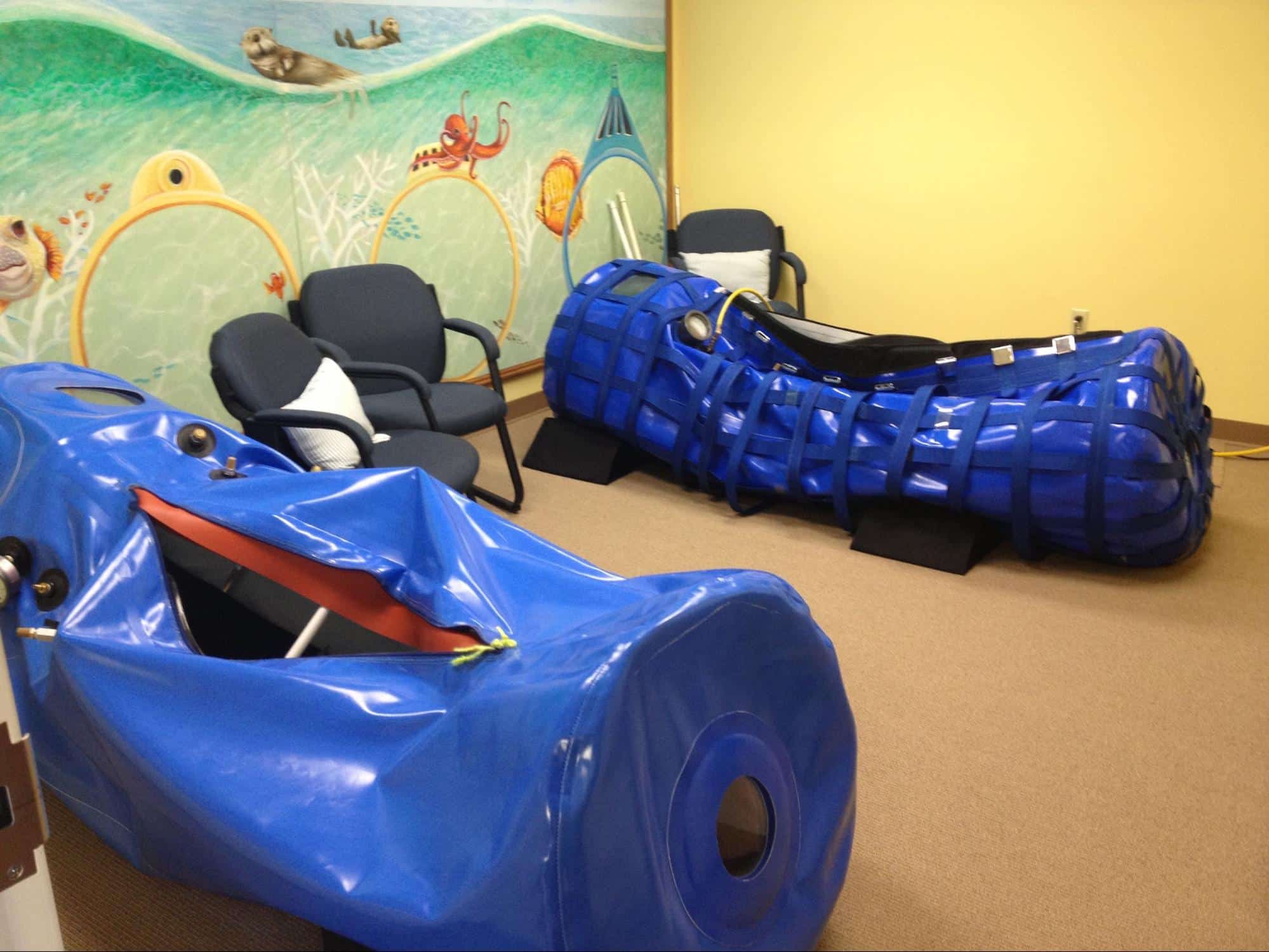
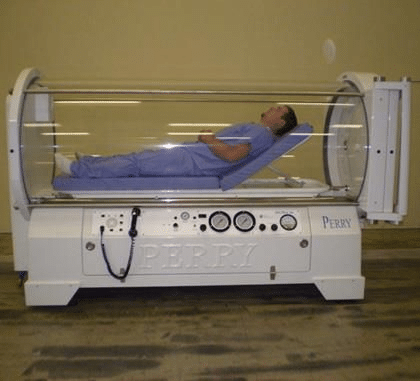
A hyperbaric chamber can be a built-in room-like structure or a movable device. It can have a monoplace design that can only accommodate one patient at a time or a multiplace design that allows for more than one person to be in the chamber at once.
In either case, hyperbaric chambers are designed with:
- Sturdy walls that can withstand the high atmospheric pressure conditions that occur in the chamber.
- Very effective seals that prevent pressure loss or oxygen leaks when the chamber is in use.
- Operational controls to regulate the pressure and oxygen conditions.
- Provisions for patients and medical personnel to either sit or lie down during hyperbaric therapy sessions.
- Modern versions now also come with communication channels. They enable people in the chamber to communicate with those outside the chamber without needing to open it; it is a rather detailed process that can disrupt a therapy session.
Functions of Hyperbaric Chambers
The higher atmospheric pressure and oxygen flow in hyperbaric chambers promote wellness in different ways. They:
- Promote healing of wounds
- Treat decompression sickness in divers
- Aid in the treatment of critical conditions like carbon monoxide poisoning and pulmonary(air) embolisms.
We will expound more on these applications below. However, for better context, let us first look at how hyperbaric therapy works.
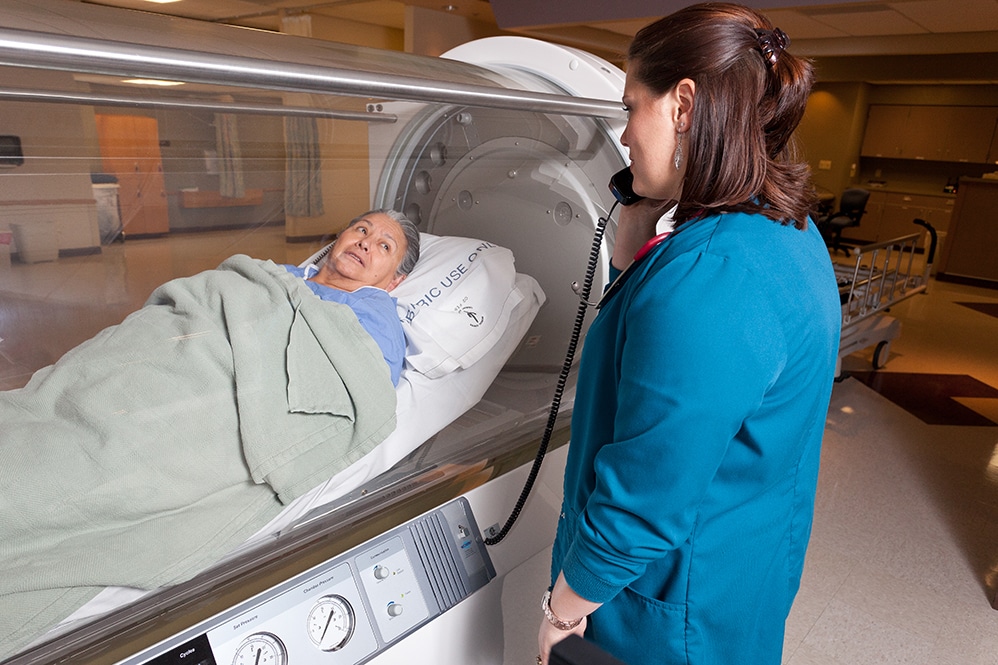
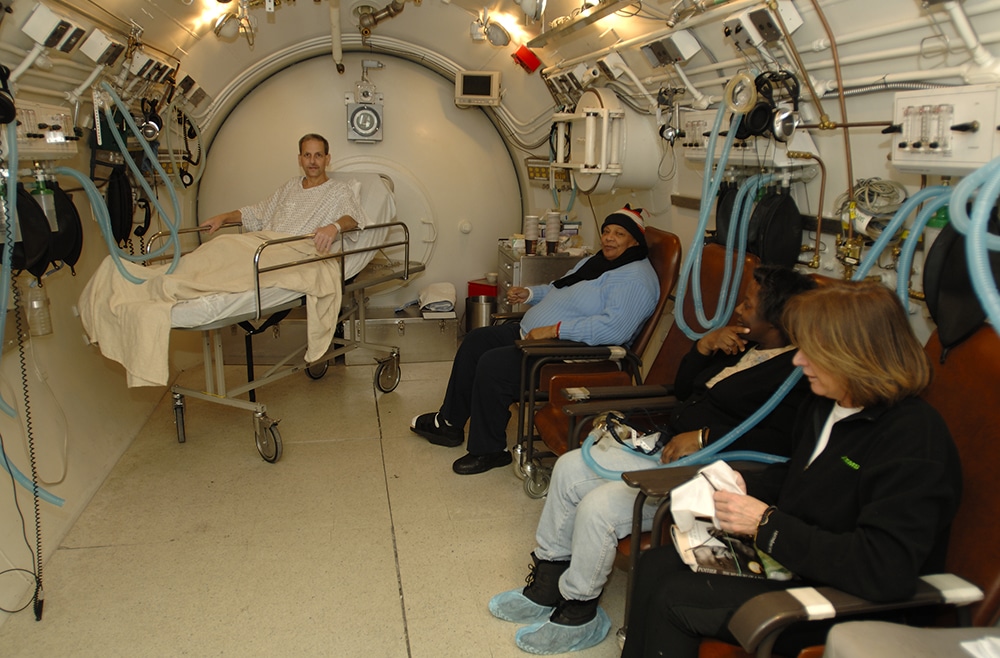
How it Works
Source: pennmedicine.org
Medical protocols require that a patient is first examined by a professional doctor before they begin hyperbaric therapy. If the doctor finds it necessary and suitable, the patient can then be placed in the chamber for therapy to begin.
In some instances, like with a monoplace hyperbaric chamber, a patient can go in alone. While in others, such as if a patient needs monitoring during therapy, both the patient and a medical professional can go into the chamber (if it is a multiplace hyperbaric chamber).
Ambient pressure and oxygen levels are then activated for therapy to begin. The pressurisation of the chamber happens gradually until it reaches the required levels. This is done to ensure safety and wellness; instant pressurisation can be fatal and pose other risks.
The duration and number of sessions that a patient requires can vary depending on their condition and the recommended medical guidance for its treatment.
Hyperbaric Chambers: The Backstory

Source: oobject.com
The whole concept of hyperbaric chambers rests on one simple principle: changes in atmospheric pressure affect the amount of oxygen that human bodies take in.
When atmospheric pressure is high, your lungs will work to take in more oxygen compared to when you are in an environment with normal or lower atmospheric pressure.
This idea first came to light in the 17th century when a British physician, Reverend Henshaw, noticed that diving underwater allows one to experience higher atmospheric pressure.
He then designed a ‘diving bell’ that allowed his patients to dive and stay underwater for the few minutes that they could tolerate. It may not have been effective at healing but the patients, at the least, felt rejuvenated by the change in pressure.
Innovative minds then continued making advancements on this idea as centuries went by. Here is a summary of some key moments in the advancement of hyperbaric chambers.
19th Century
Around 1830, Paul Bert ran research trials on the effects that higher atmospheric pressure has on animals. The French doctor documented informative findings that, for the first time, shed light on the cause and effect of decompression sickness.
20th Century
Another French doctor and surgeon, Orézzoli, went a step further in 1917 and successfully used high-pressure oxygen to treat a soldier suffering from gas gangrene.
Rudimentary hyperbaric chamber designs thus began to emerge later in the century. The U.S. Navy was at the forefront of this development as it learned that the chambers could help save their soldiers from decompression sickness during World War II.
The experimental phase of treatments was so successful that a regulatory body had been established to oversee the advancement of hyperbaric therapy by the end of the century.
The design, technology, and efficiency of hyperbaric chambers has been on an upward trend ever since.
Applications of Hyperbaric Chambers
Hyperbaric chambers are mainly used in medical and wellness treatments. That is, however, a very broad statement. So, let us look into more specific applications.
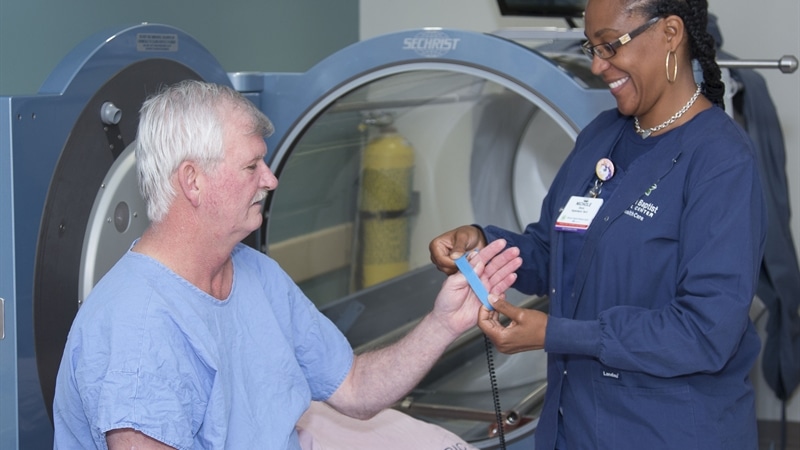
Medical Applications
Source: missouribaptist.org
The high atmospheric pressure and oxygen levels in a hyperbaric chamber make it possible for more oxygen to reach the cells and tissues in a patient’s body.
The high pressure, in particular, enables cells and tissues to absorb more oxygen than they ordinarily would. This influx of oxygenated blood throughout the body promotes cell regeneration, clearing of waste from the body, and generally improves immunity.
This is, therefore, why and how hyperbaric oxygen therapy works for:
- The treatment of non-healing wounds in diabetic or immunocompromised patients
- Treating radiation injuries
- Complimenting other forms of care for cancer patients
- Carbon dioxide poisoning treatment
- Preventing or treating post-surgical infections
- Treating bone or bone marrow inflammations
- Treating sudden deafness and vision loss
- Curing decompression sickness
Veterinary Medicine Applications
It turns out Doctor Paul Bert’s findings were correct and hyperbaric oxygen therapy does have beneficial effects on animals. Mammals, to be more precise.
Just like in humans, it can promote the healing of wounds. Its use in veterinary medicine has also shown positive results in the management or treatment of:
- Neurological conditions
- Cancer
- Inflammations
- Auto-immune disorders
Sports and Performance Enhancement

Source: Pexels
Taking part in sports can offer lots of rewards but it also causes its fair share of fatigue, muscle soreness, and a higher risk for injuries.
Athletes thus turn to hyperbaric therapy because:
- It promotes faster healing and recovery from injuries.
- The influx of oxygen into their bloodstreams, during hyperbaric therapy, takes away fatigue and muscle soreness. This enables them to maintain better energy levels for games and workouts.
Pros and Cons of Hyperbaric Chambers
Pros
- Improved oxygen delivery
Oxygen-starved tissues begin to slowly die or degenerate over time. Better and higher oxygen absorption in the human body is thus a huge benefit as it prevents this by stimulating healing and cell regeneration.
- Effective treatment of decompression sickness
Decompression sickness often occurs when you resurface from a deep dive and the inert gases you absorbed during the dive form bubbles in your cells or bloodstream. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy effectively cures it by supporting your body to absorb pure oxygen and ‘flush’ out the rest of the gases.
- Reduction of swelling and inflammation
Increased pressure in hyperbaric chambers causes patients’ blood vessels to narrow thereby reducing swelling caused by edema and other conditions. Higher circulation of oxygenated blood also generally reduces inflammation.
- Complementary therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is non-invasive and is, therefore, an ideal complementary therapy for other treatments like medications, physiotherapy, and cancer treatments.
Cons
- Limited access
Hyperbaric chambers are often not available in most medical facilities due to the cost implications and the fact that they require specialised personnel to manage them.
- Side effects
Patients may experience ENT discomfort, temporary changes in vision, and fatigue after hyperbaric therapy sessions. More severe side effects like lung collapse or oxygen toxicity are rare but can occur.
- Cost
The cost of seeking multiple hyperbaric therapy sessions can be too high for most patients if it is not mitigated by insurance coverage.
Emerging Trends in Hyperbaric Chambers

Source: oxygenark
Hyperbaric chambers are today more broadly embraced in medical and wellness practice than ever before. This is due to:
- An increase in manufacturers and design options that makes it easier to be able to buy a hyperbaric chamber.
- Relatively lower prices compared to the earlier years.
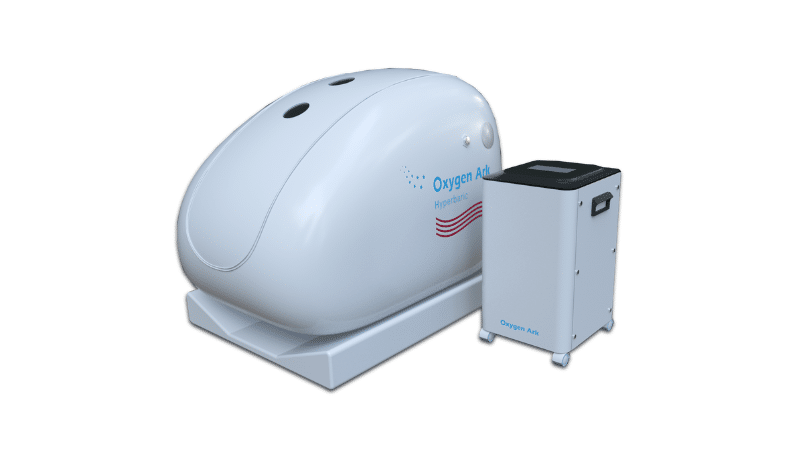
Additionally, innovative firms like Oxygenark now also produce hyperbaric chamber models that you can safely use in your home, private medical practice, or wellness center. This is a major boost to breaking the access barrier.
The designs are equally far more user-friendly. Structure-wise, you can find lightweight designs,pact designs if you are pressed for space, and a variety of mono or multiplace options.
The controls, in modern designs, are easier and safer to use as well. They include convenient touchscreen panels, chamber locking sensors, and quieter running.
In Conclusion
Hyperbaric chambers may sound like a relic from the past but they are undoubtedly the future of medicine. More so as the world embraces alternative approaches to healing and issues like air pollution continue to pose a threat to our immune systems.